News

Flood Plain Mapping

By Ellen Enslin, CPESC, Program Manager
It’s hurricane season, which unfortunately means there is a chance for heavy rains to cause flooding in Northeast Pennsylvania. In some areas we have already seen these impacts. All that rain eventually finds its way over the land, and into streams and their associated floodplains. Floodplains are lowland areas next to streams and rivers that are prone to inundation by water during flood events.
Some terms to know:
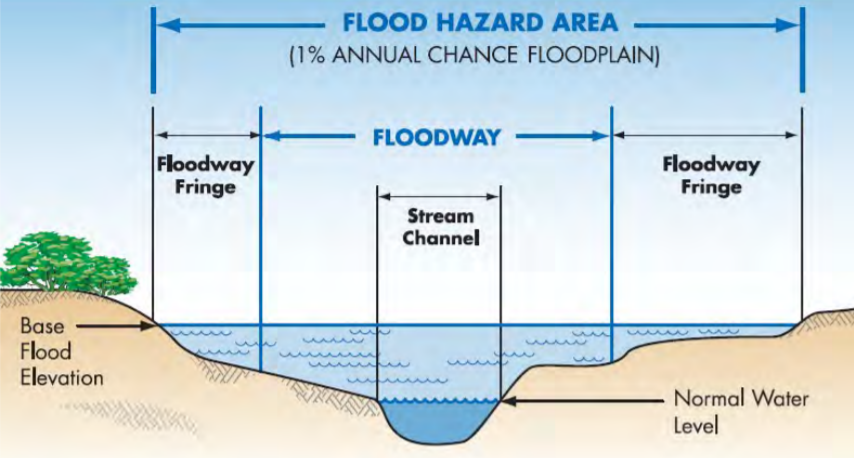
The “100-year” floodplain is commonly referred to and includes the area that would be inundated by a flood having a 1% chance of occurring in any given year.
A “100-year” flood can occur during any given year or multiple times a year, if the conditions are right.
A floodway is a part of the larger floodplain and includes the stream channel and portions of the adjoining floodplain.
Floodplains often contain wetlands and other areas that are vital to a diverse and healthy stream ecosystem. The floodway must be preserved to allow the discharge of the base flood without increasing flood heights more than a designed amount. By regulation in Pennsylvania, the floodway, in areas that do not have a detailed floodplain mapping is assumed, absent evidence to the contrary, to extend 50 feet back from the top of bank on both sides of the stream.
Floodplains perform a variety of functions that are valuable to humans and fish and wildlife species. Important functions of stream floodplains include flood water storage, water quality maintenance, erosion control, fish and wildlife habitat, and recreation/open space.
Activities in a floodplain can have negative impacts both within a property as well as in areas located upstream or downstream. Removing vegetation, compacting soil, and placing fill or structures in floodplains all have the potential to diminish the flow capacity of the floodplains, increasing flow velocities in streams and raise flood levels so areas formerly not at risk become endangered. Patterns of flow may also change, potentially increasing erosion and damaging infrastructure and streamside properties.
The ability of floodplains to carry and store floodwaters should be preserved and respected so we can reduce infrastructure and property damage, protect critical natural and cultural resources, and promote sustainable development of our communities.
For more information about floodplains or to determine if an area of land is within a floodplain, please consult the FEMA maps: https://www.fema.gov/flood-maps
Additional information in Pennsylvania can also be located here: https://www.pema.pa.gov/Pages/default.aspx and https://pafloodrisk.psu.edu/